GENETICS
4. The Chromosome theory of heredity

Seven pairs of identical twins. Although the twins were given no instructions regarding how to pose for the
photograph, note the similar posture, hand placement, and facial expressions of bother members
of each pair of twins.
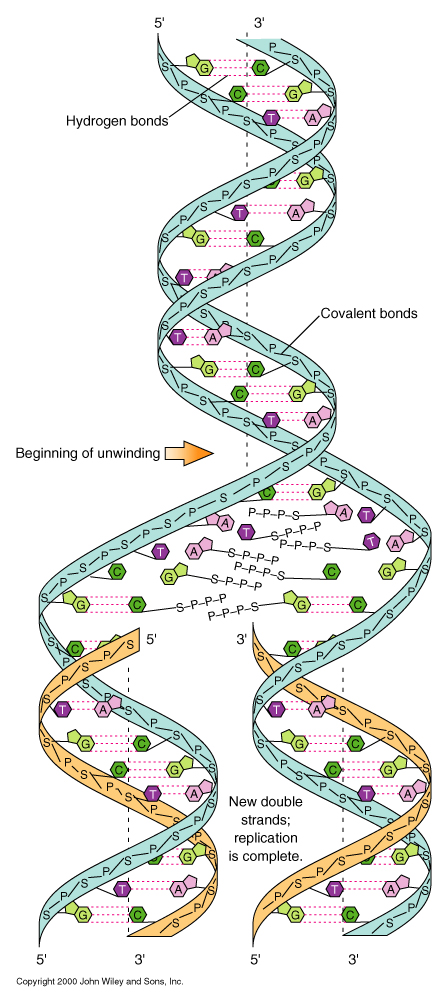
DNA replication is a precursor to asexual and sexual cell division.
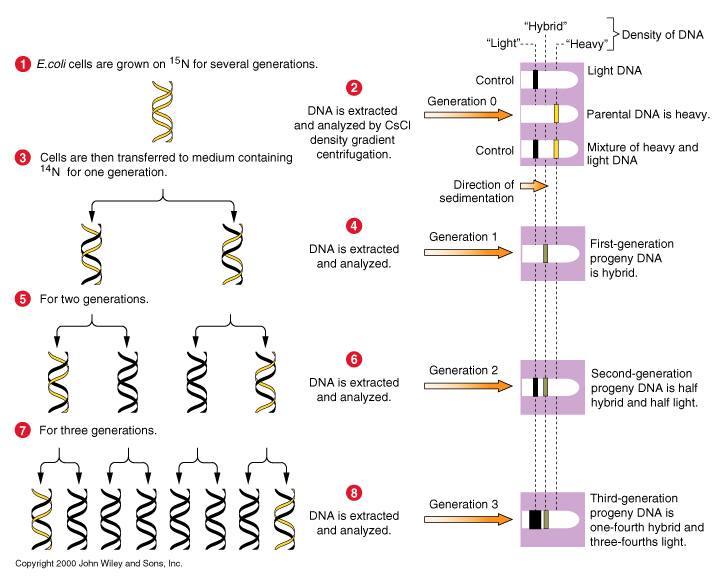
DNA replicates by unwinding and using the exposed strands as alignment guides for new synthesis; hence, each daughter molecule is half old and half new. = "semiconservative replication"
DNA polymrase adds nucleotides at 3' growing.
-
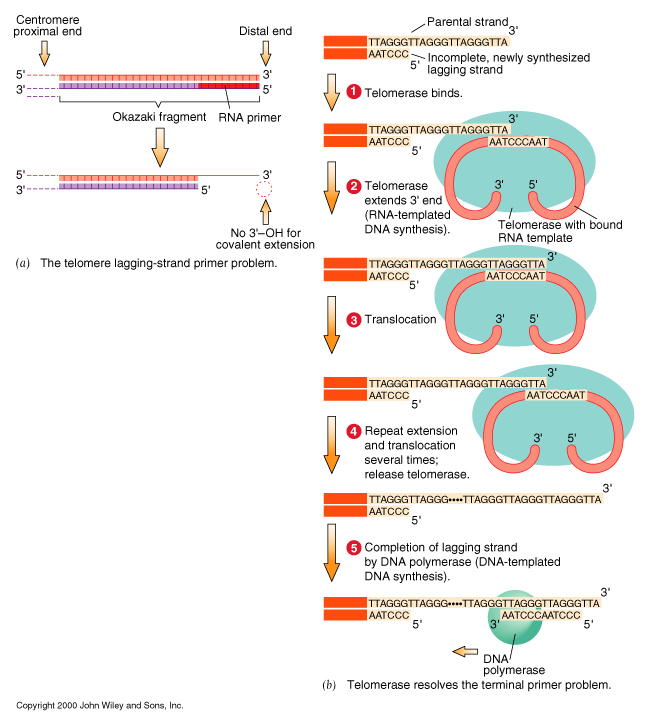
Telomerase: replication of linear chromosome termini
Phenotypic ratios in progeny are determined by the movements of chromosome pairs at meiosis.
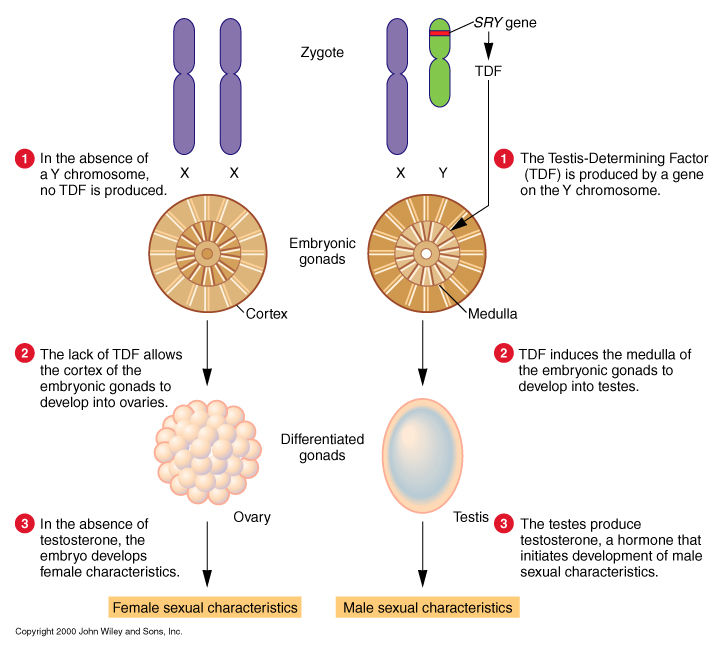
Chromosome theory: 1910, Thomas Morgan
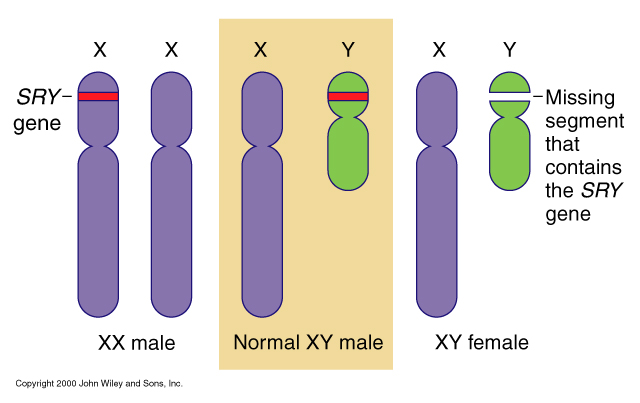
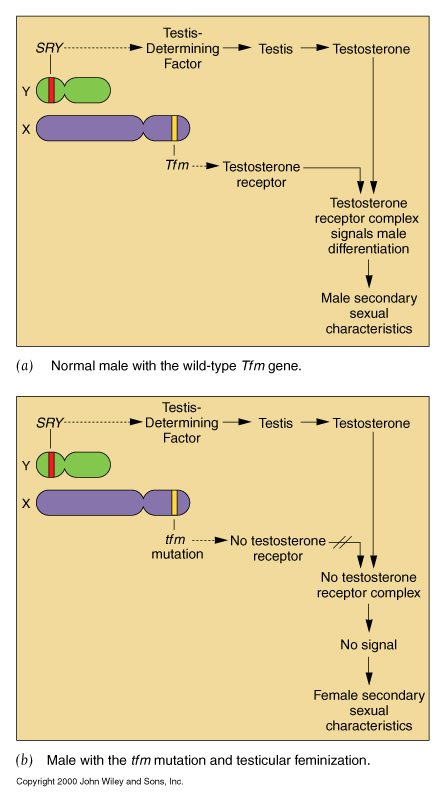
genes are situated on chromosomes sex chromosome-linked genes
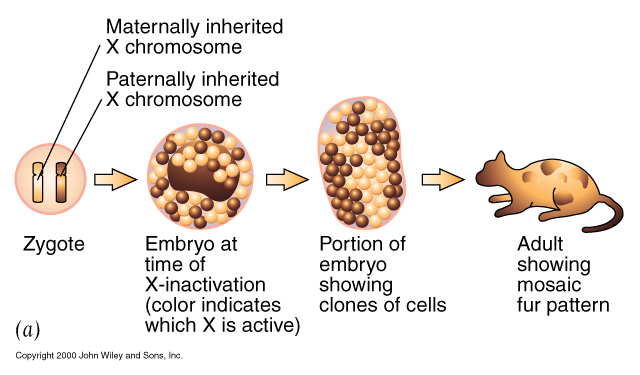
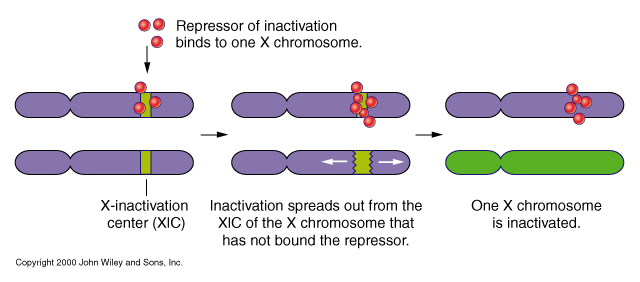
X-inactivation
-
Organelle genes (mitochondria, chloroplast) are inherited maternally.
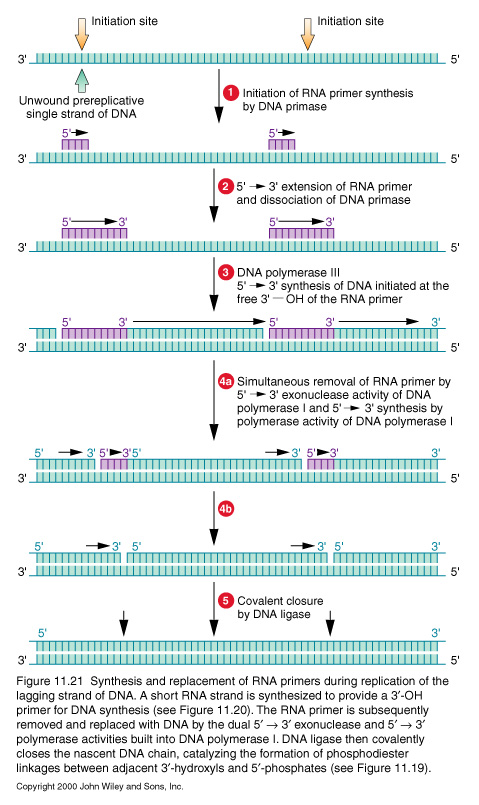
- replication starts at the origin site:
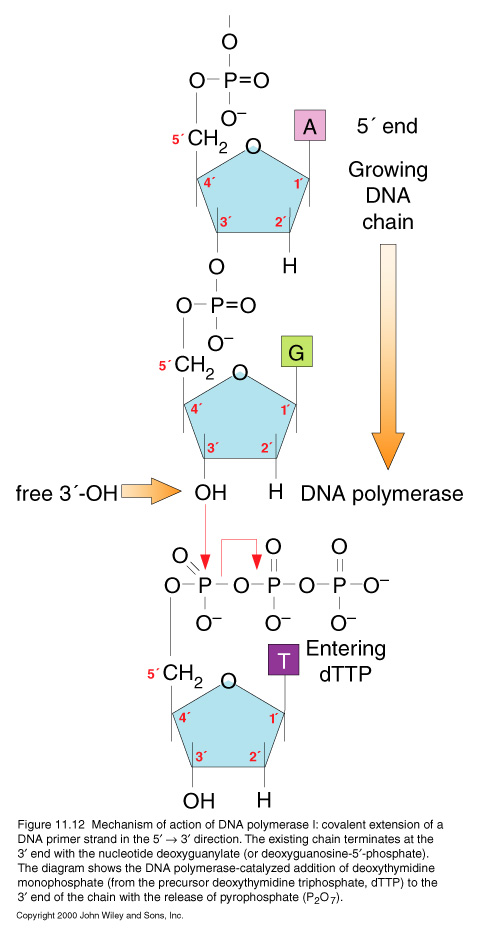
- proofreading by the DNA polymerase
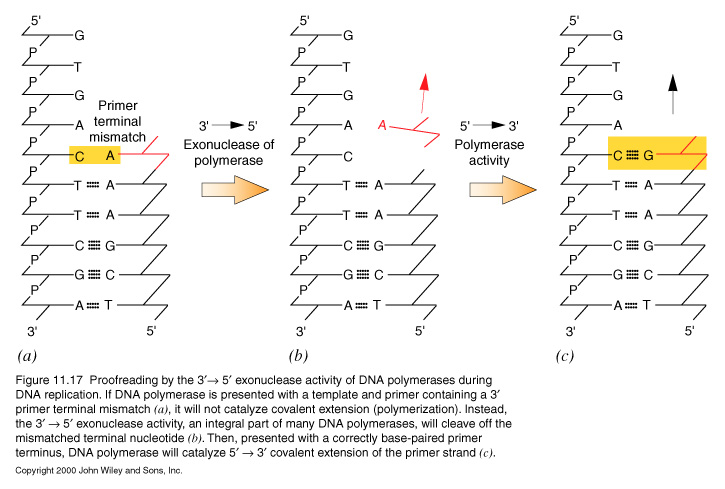
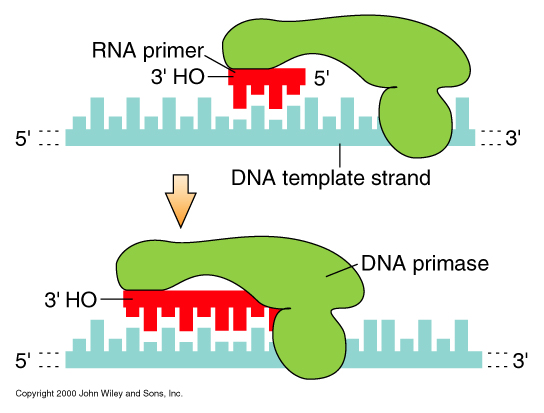
- DNA polymerase requires 'PRIMER':
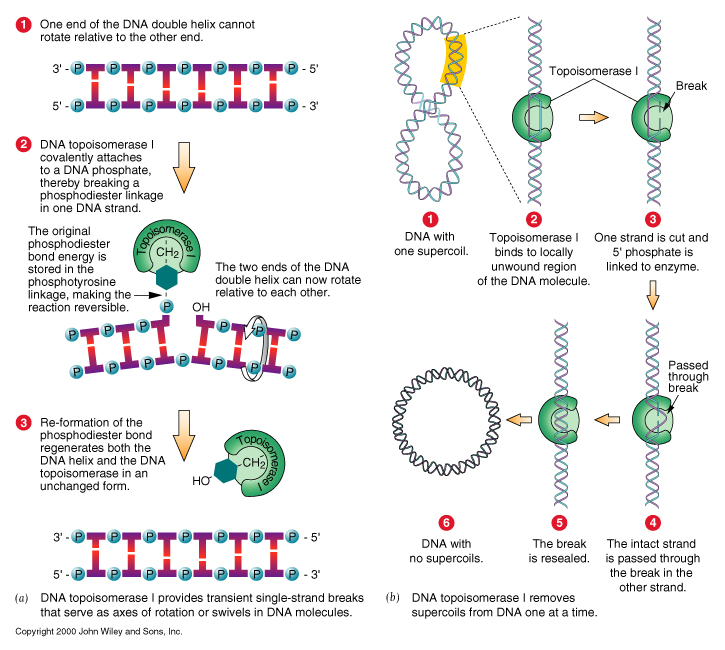
- DNA topoisomerases (I & II) prevent DNA from becoming tangled ahead of
the replication fork:
DNA topoisomerase II: cuts both strand of DNA and rejoin the ends
to produce one negative superturn.
- DNA polymerase can't synthesize DNA at the terminus of the lagging strand.
- Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment.
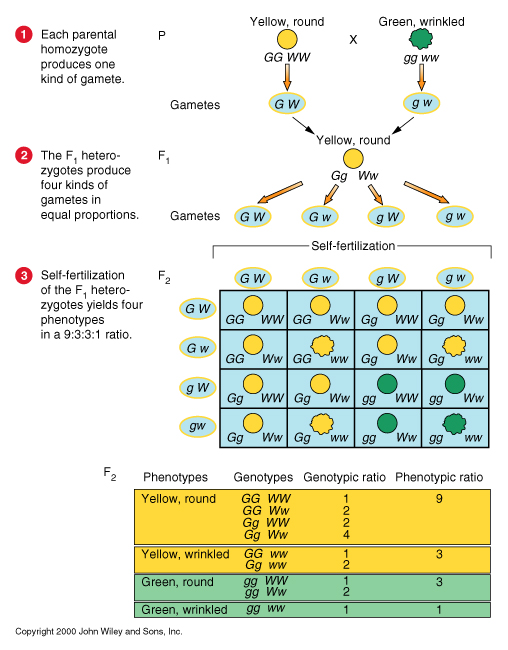
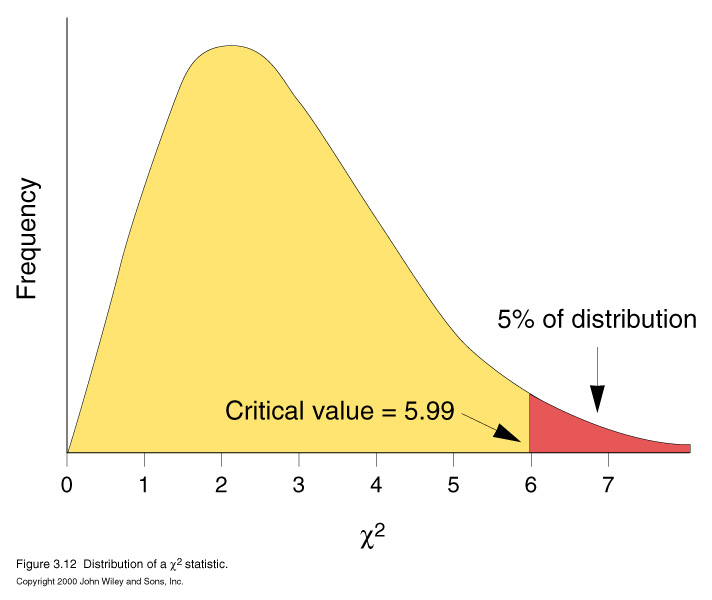
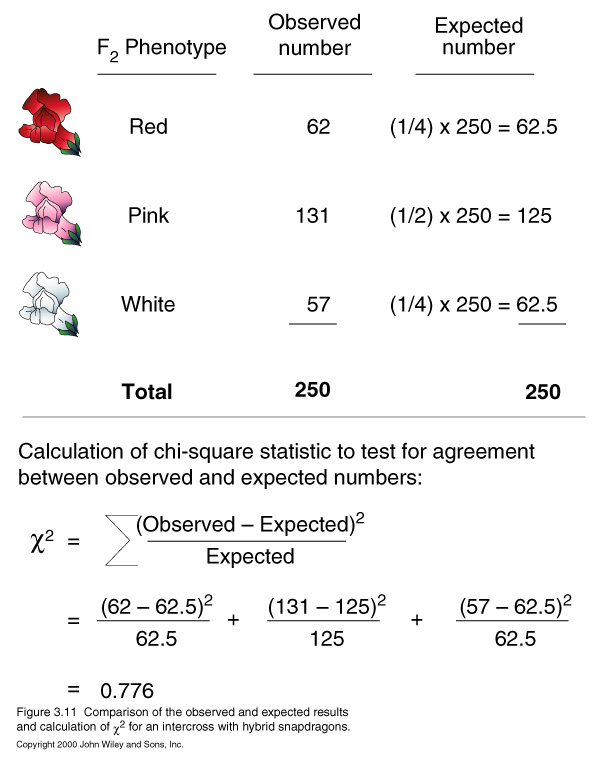
- chi square test : test of fitness of a hypothesis
The distribution of chi-square values shows how often chi-square will exceed a particular value
solely by chance. If the hypothesis is correct, the chi-square statistic will exceed
this critical value only 5 percent of time.
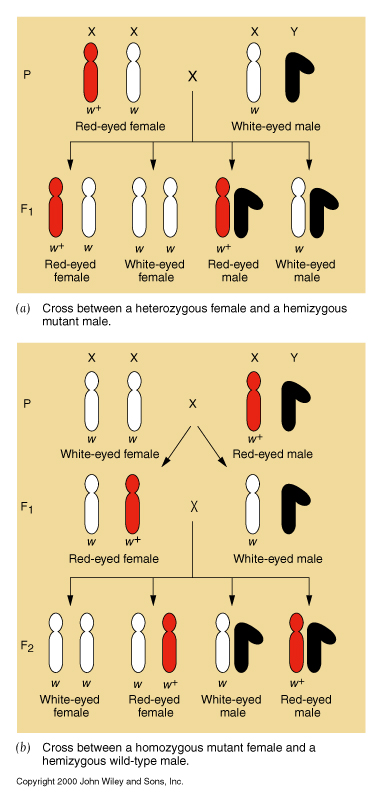
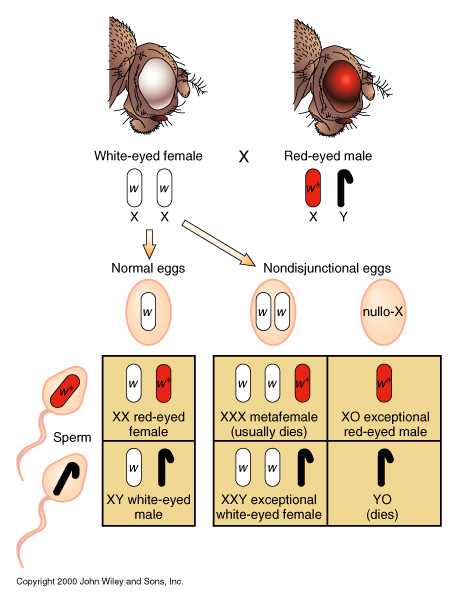
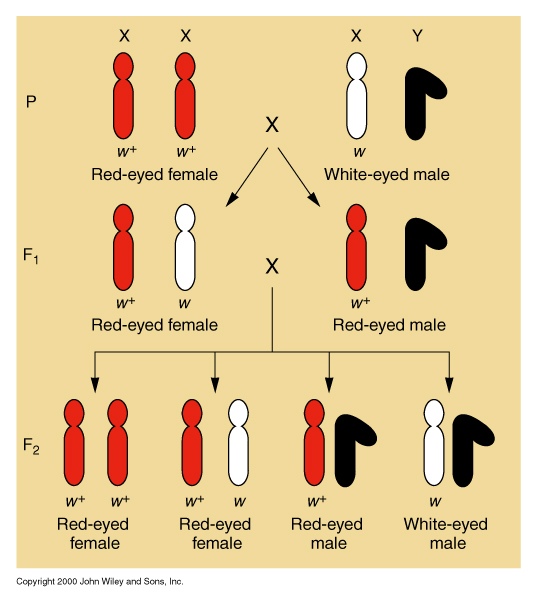
- Genes for eye color are linked to the X chromosome:
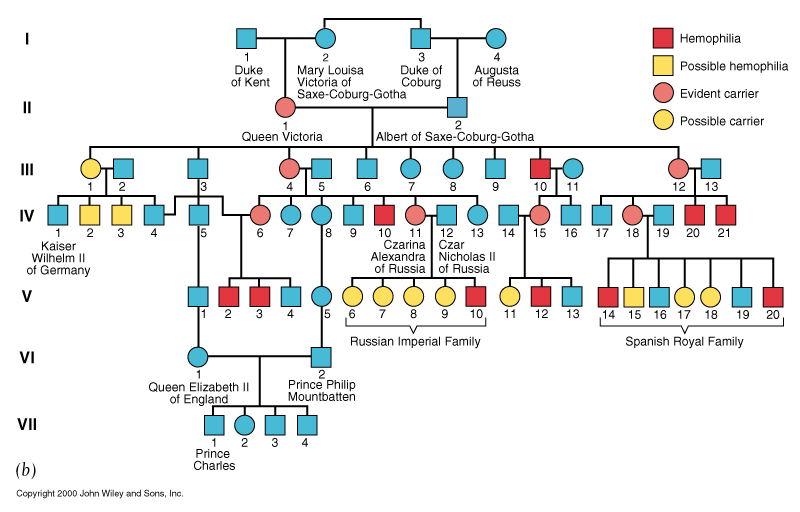 Hemophilia
Hemophilia